Checkpoint Protein Expression in Tumor Microenvironment Defines Prognosis of Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 04 Jan 2022 |

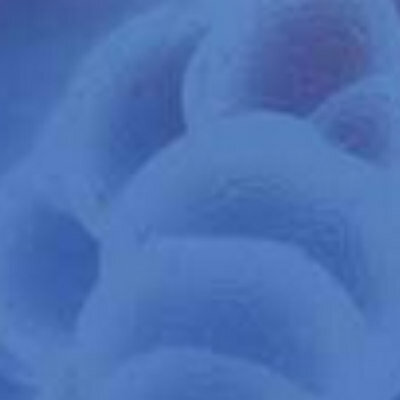
Image: Bone marrow aspirate from a patient with classical Hodgkin Lymphoma with large multinucleated Reed-Sternberg cells. “Hodgkin cells” are mononuclear while “Reed-Sternberg” cells are multinucleate forms (Photo courtesy of Nidia P. Zapata, MD and Espinoza-Zamora Ramiro)
In Hodgkin lymphoma, B-lymphocytes start to multiply in an abnormal way and begin to collect in certain parts of the lymphatic system, such as the lymph nodes (glands). The affected lymphocytes lose their infection-fighting properties, making one more vulnerable to infection.
In classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), sparse malignant Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells are embedded into extensive tumor microenvironment (TME) consisting mostly of benign immune cells, such as T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, eosinophils, plasma cells, and mast cells.
Clinical Scientists at the Helsinki University Hospital (Helsinki, Finland) and their colleagues studied clinical data and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) diagnostic tumor tissue samples from patients with primary cHL diagnosed between years 1993- 2012 and treated or followed. The patients were divided into two cohorts: the first cohort, “gene expression cohort”, consisted of 88 patients, and the second cohort, “immunohistochemistry (IHC) cohort”, of 131 patients.
The scientists used the NanoString nCounter digital gene expression profiling with 770-gene PanCancer Immune Profiling Panel (XT-CSO-HIP1-12, NanoString Technologies, Seattle, WA, USA) for gene expression profiling. To assess the proportions of the distinct immune cells in the TME, they applied CIBERSORT (Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA) for the gene expression cohort, and multiplex immunohistochemistry to characterize the immunoprofile of cHL TME, and correlated the findings with survival. Gene expression analysis divided tumors into subgroups with T cell-inflamed and non-inflamed TME. Several macrophage-related genes were upregulated in samples with the non-T cell-inflamed TME, and based on the immune cell proportions, the samples clustered according to the content of T cells and macrophages.
The investigators reported that a cluster with high proportions of checkpoint protein (PD-1, PD-L1, IDO-1, LAG-3, and TIM-3) positive immune cells translated to unfavorable overall survival (OS) (5-year OS 76% vs. 96%), and remained as an independent prognostic factor for OS in multivariable analysis (HR 4.34). cHLs with high proportions of checkpoint proteins overexpressed genes coding for cytolytic factors, proposing paradoxically that they were immunologically active. This checkpoint molecule gene signature translated to inferior survival in a validation cohort of 290 diagnostic cHL samples and in an expansion cohort of 84 cHL relapse samples.
The authors concluded that their findings provide novel, more accurate information on the composition of different immune cells, checkpoint molecules, and their relationship in the heterogeneous cHL TME. Furthermore, the data recognize the prognostic impact of T cell and Tumor-Associated Macrophage (TAM) mediated checkpoint molecules on the survival of cHL patients. The study was published on December 23 2021 in the journal Blood Advances.
Related Links:
Helsinki University Hospital
NanoString Technologies
CIBERSORT
In classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), sparse malignant Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells are embedded into extensive tumor microenvironment (TME) consisting mostly of benign immune cells, such as T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, eosinophils, plasma cells, and mast cells.
Clinical Scientists at the Helsinki University Hospital (Helsinki, Finland) and their colleagues studied clinical data and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) diagnostic tumor tissue samples from patients with primary cHL diagnosed between years 1993- 2012 and treated or followed. The patients were divided into two cohorts: the first cohort, “gene expression cohort”, consisted of 88 patients, and the second cohort, “immunohistochemistry (IHC) cohort”, of 131 patients.
The scientists used the NanoString nCounter digital gene expression profiling with 770-gene PanCancer Immune Profiling Panel (XT-CSO-HIP1-12, NanoString Technologies, Seattle, WA, USA) for gene expression profiling. To assess the proportions of the distinct immune cells in the TME, they applied CIBERSORT (Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA) for the gene expression cohort, and multiplex immunohistochemistry to characterize the immunoprofile of cHL TME, and correlated the findings with survival. Gene expression analysis divided tumors into subgroups with T cell-inflamed and non-inflamed TME. Several macrophage-related genes were upregulated in samples with the non-T cell-inflamed TME, and based on the immune cell proportions, the samples clustered according to the content of T cells and macrophages.
The investigators reported that a cluster with high proportions of checkpoint protein (PD-1, PD-L1, IDO-1, LAG-3, and TIM-3) positive immune cells translated to unfavorable overall survival (OS) (5-year OS 76% vs. 96%), and remained as an independent prognostic factor for OS in multivariable analysis (HR 4.34). cHLs with high proportions of checkpoint proteins overexpressed genes coding for cytolytic factors, proposing paradoxically that they were immunologically active. This checkpoint molecule gene signature translated to inferior survival in a validation cohort of 290 diagnostic cHL samples and in an expansion cohort of 84 cHL relapse samples.
The authors concluded that their findings provide novel, more accurate information on the composition of different immune cells, checkpoint molecules, and their relationship in the heterogeneous cHL TME. Furthermore, the data recognize the prognostic impact of T cell and Tumor-Associated Macrophage (TAM) mediated checkpoint molecules on the survival of cHL patients. The study was published on December 23 2021 in the journal Blood Advances.
Related Links:
Helsinki University Hospital
NanoString Technologies
CIBERSORT
Latest Hematology News
- Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
- First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
- POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
- Handheld White Blood Cell Tracker to Enable Rapid Testing For Infections
- Smart Palm-size Optofluidic Hematology Analyzer Enables POCT of Patients’ Blood Cells
- Automated Hematology Platform Offers High Throughput Analytical Performance
- New Tool Analyzes Blood Platelets Faster, Easily and Accurately
- First Rapid-Result Hematology Analyzer Reports Measures of Infection and Severity at POC
- Bleeding Risk Diagnostic Test to Reduce Preventable Complications in Hospitals
- True POC Hematology Analyzer with Direct Capillary Sampling Enhances Ease-of-Use and Testing Throughput
- Point of Care CBC Analyzer with Direct Capillary Sampling Enhances Ease-of-Use and Testing Throughput
- Blood Test Could Predict Outcomes in Emergency Department and Hospital Admissions
- Novel Technology Diagnoses Immunothrombosis Using Breath Gas Analysis
- Advanced Hematology System Allows Labs to Process Up To 119 Complete Blood Count Results per Hour
- Unique AI-Based Approach Automates Clinical Analysis of Blood Data
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
Mass spectrometry is a precise technique for identifying the chemical components of a sample and has significant potential for monitoring chronic illness health states, such as measuring hormone levels... Read more.jpg)
POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
Exosomes, tiny cellular bioparticles carrying a specific set of proteins, lipids, and genetic materials, play a crucial role in cell communication and hold promise for non-invasive diagnostics.... Read more
Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
The conventional methods for measuring free cortisol, the body's stress hormone, from blood or saliva are quite demanding and require sample processing. The most common method, therefore, involves collecting... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Unique Autoantibody Signature to Help Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis Years before Symptom Onset
Autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) are thought to occur partly due to unusual immune responses to common infections. Early MS symptoms, including dizziness, spasms, and fatigue, often... Read more
Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is known to cause various cancers, including those of the genitals, anus, mouth, throat, and cervix. HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer (HPV+OPSCC) is the most common HPV-associated... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Mouth Bacteria Test Could Predict Colon Cancer Progression
Colon cancer, a relatively common but challenging disease to diagnose, requires confirmation through a colonoscopy or surgery. Recently, there has been a worrying increase in colon cancer rates among younger... Read more.jpg)
Unique Metabolic Signature Could Enable Sepsis Diagnosis within One Hour of Blood Collection
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition triggered by an extreme response of the body to an infection. It requires immediate medical intervention to prevent potential death or lasting damage.... Read morePathology
view channel
Spatial Tissue Analysis Identifies Patterns Associated With Ovarian Cancer Relapse
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma is the most lethal type of ovarian cancer, and it poses significant detection challenges. Typically, patients initially respond to surgery and chemotherapy, but the... Read more.jpg)
Unique Hand-Warming Technology Supports High-Quality Fingertip Blood Sample Collection
Warming the hand is an effective way to facilitate blood collection from a fingertip, yet off-the-shelf solutions often do not fulfill laboratory requirements. Now, a unique hand-warming technology has... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
While PCR tests are the gold standard of accuracy for virology testing, they come with limitations such as complexity, the need for skilled lab operators, and longer result times. They also require complex... Read more
DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), recognized for its potential to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene, is a material that's increasingly catching the eye of the scientific community.... Read more
Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
Microfluidics, which are miniature devices that control the flow of liquids and facilitate chemical reactions, play a key role in disease detection from small samples of blood or other fluids.... Read more
Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
Home testing gained significant importance during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet the availability of rapid tests is limited, and most of them can only drive one liquid across the strip, leading to continued... Read moreIndustry
view channel
ECCMID Congress Name Changes to ESCMID Global
Over the last few years, the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID, Basel, Switzerland) has evolved remarkably. The society is now stronger and broader than ever before... Read more
Bosch and Randox Partner to Make Strategic Investment in Vivalytic Analysis Platform
Given the presence of so many diseases, determining whether a patient is presenting the symptoms of a simple cold, the flu, or something as severe as life-threatening meningitis is usually only possible... Read more
Siemens to Close Fast Track Diagnostics Business
Siemens Healthineers (Erlangen, Germany) has announced its intention to close its Fast Track Diagnostics unit, a small collection of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing products that is part of the... Read more